Controlling the RobotsConf Sumobot with Spark Core & Johnny-Five
Posted by Rick Waldron
In the previous article, I walked through inventory, preparation, calibration and assembly of the SumoBot Kit that was provided to all attendees of this year’s RobotsConf.
In this article, I’m going introduce a simple program to for controlling the assembled SumoBot with a Spark Core. This entire article will assume that you have already read Assembling and Preparing the RobotsConf Sumobot with Johnny-Five and completed all of the preparatory and assembly tasks described therein.
Spark Core
The Spark Core is available in a single form factor, as shown on their site. Here’s the Spark Core entry from the Board Selection section of Assembling and Preparing the RobotsConf Sumobot with Johnny-Five:
| Board | # Pins | # Digital IO | # Analog IO | # PWM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spark Core | 16 | 16 | 8 | 8 |
Note that communication with the Spark Core requires internet connected Wi-Fi and provides a couple options for setting up the connection.
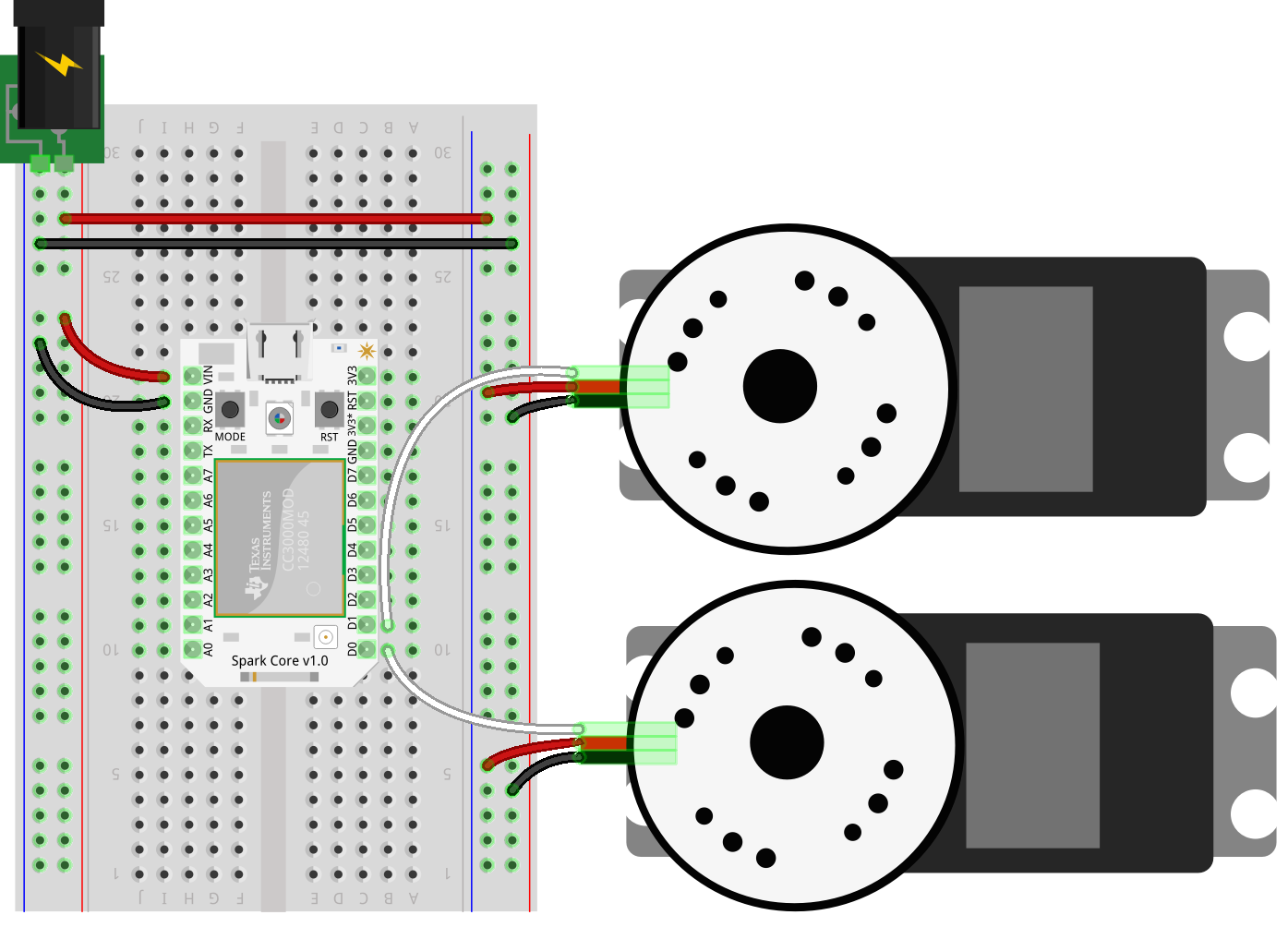
SumoBot Circuit
Here’s the fully assembled circuit, attached to the bot:
Controlling The SumoBot
The controller program has been adapted from the original program provided in the SumboBot Jr. repo and is available via npm. The controls library, keypress, must also be installed.
npm install keypress sumobot
The keypress module will turn your laptop into a remote control device for the SumoBot, using the following keys -> command mappings:
| Key | Command |
|---|---|
| Arrow Up | Forward |
| Arrow Down | Reverse |
| Arrow Left | Turn Left |
| Arrow Right | Turn Right |
| Space | Stop |
| q | Quit |
var keypress = require("keypress");
var Spark = require("spark-io");
var five = require("johnny-five");
var Sumobot = require("sumobot")(five);
keypress(process.stdin);
var board = new five.Board({
io: new Spark({
token: process.env.SPARK_TOKEN,
deviceId: process.env.SPARK_DEVICE_2
})
});
board.on("ready", function() {
console.log("Welcome to Sumobot Jr!");
// Initialize a new Sumobot.
// - Left Servo is attached to pin D0
// - Right Servo is attached to pin D1
// - Speed set to 0.50 (half of max speed)
//
var bot = new Sumobot({
left: "D0",
right: "D1",
speed: 0.50
});
// Maps key names to bot methods
var actions = {
up: "fwd",
down: "rev",
left: "left",
right: "right",
space: "stop"
};
// Ensure the bot is stopped
bot.stop();
// A bit of keypress ceremony ;)
process.stdin.resume();
process.stdin.setEncoding("utf8");
process.stdin.setRawMode(true);
process.stdin.on("keypress", function(ch, key) {
var action;
if (!key) {
return;
}
action = actions[key.name] || key.name;
if (action == "q") {
console.log("Quitting");
bot.stop();
setTimeout(process.exit, 500);
}
if (bot[action]) {
bot[action]();
}
});
});
Next Steps
Now that you know how to control the SumoBot, think about ways that you might want to extend its capabilities. In the final article of this series, I will introduce some simple customizations that will add some interesting character to your project.